Vue 初始化
不管我们在使用 Vue Cli 生成的框架,还是直接 script 标签引入的 Vue,在使用 Vue 的时候,都需要 new Vue(); 原因上一篇已经讲过,Vue 是一个函数类,只能通过 new 来创建一个实例,从而来使用。
这篇我们来看一下 Vue 初始化的过程,我们在第一篇里创建了调试环境,我们就在 new Vue 的时候打一个断点,来看看 Vue 初始化都做了哪些事情。
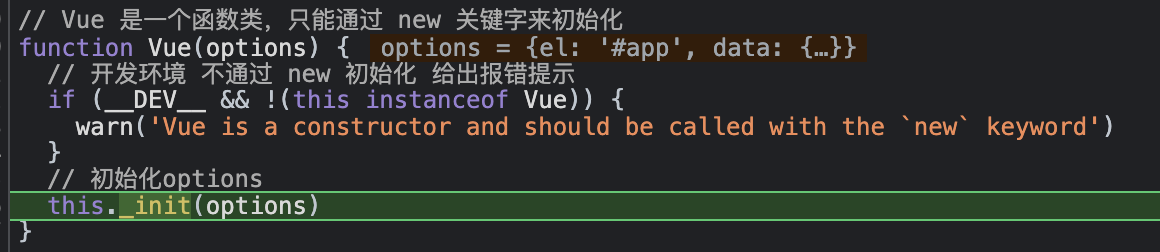
在 new Vue() 的时候,进入到了 Vue 的方法里,并执行了this._init(options)这个方法, 这个方法是从哪来的呢?
我们继续调试,进入了initMixin 这个方法里,我们来研究一下这个方法, 这个方法
在/core/instance/init.ts中
import config from '../config';
import { initProxy } from './proxy';
import { initState } from './state';
import { initRender } from './render';
import { initEvents } from './events';
import { mark, measure } from '../util/perf';
import { initLifecycle, callHook } from './lifecycle';
import { initProvide, initInjections } from './inject';
import { extend, mergeOptions, formatComponentName } from '../util/index';
import type { Component } from 'types/component';
import type { InternalComponentOptions } from 'types/options';
import { EffectScope } from 'v3/reactivity/effectScope';
let uid = 0;
// 初始化mixin
export function initMixin(Vue: typeof Component) {
// _init 方法 只有一个参数 options
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Record<string, any>) {
const vm: Component = this;
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++;
// 用于测试代码性能
let startTag, endTag;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__DEV__ && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`;
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`;
mark(startTag);
}
// 一个标志来标记它为Vue实例,从而不用执行instanceof检查
vm._isVue = true;
// 避免实例被观察到
vm.__v_skip = true;
// effect scope
vm._scope = new EffectScope(true /* detached */);
vm._scope._vm = true;
// 合并 options
// 有子组件时,_isComponent 为true
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// 优化内部组件实例化,因为动态选项合并非常慢,而且没有任何内部组件选项需要特殊处理。
initInternalComponent(vm, options as any);
} else {
// Vue 实例不是组件时
// 就会给$options 属性赋值一个 合并的options
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
// 解析constructor上的options属性的
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor as any),
options || {}, // 传入的 options
vm, // 该实例 this
);
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 给 _renderProxy 属性赋值,不同环境赋值的结果不同
if (__DEV__) {
initProxy(vm);
} else {
// 属性指向 vue 实例本身
vm._renderProxy = vm;
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm;
initLifecycle(vm); // 初始化生命周期相关字段
initEvents(vm); // 初始化事件列表
// 处理插槽和作用于插槽,提供_c和$createElement函数用于创建VNode,接收父组件传递$attrs和$listeners作为响应式数据
initRender(vm);
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate', undefined, false /* setContext */); //执行 beforeCreate生命周期钩子
initInjections(vm); // 在 data/props 之前初始化 inject
initState(vm); // // 初始化 data,props,methods computed,watch
initProvide(vm); // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created'); // 执行 created 生命周期钩子
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__DEV__ && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false);
mark(endTag);
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag);
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el);
}
};
}
// 初始化合并选项
// 主要做两件事: 1、指定组件 $options 原型
// 2、把组件依赖于父组件的props、listeners也挂载到options上,方便子组件调用
export function initInternalComponent(
vm: Component, // 组件实例 即this
options: InternalComponentOptions, // createComponentInstanceForVnode中定义的组件options
) {
// 把组件构造函数的 options 挂载到 vm.$options 的 __proto__ 上
const opts = (vm.$options = Object.create((vm.constructor as any).options));
// 把传入参数的 option 的 _parentVode 和 parent 挂载到组件实例 $options 上
// 这样做是因为它比动态枚举更快.
const parentVnode = options._parentVnode; // 组件 Vnode 对象
opts.parent = options.parent; // 根实例
opts._parentVnode = parentVnode;
// 父组件里的 vnode 上的
// propsData,listeners,children,tag属性挂载到 $options 上
const vnodeComponentOptions = parentVnode.componentOptions!;
opts.propsData = vnodeComponentOptions.propsData; // props
opts._parentListeners = vnodeComponentOptions.listeners; // 子组件emit出来的方法
opts._renderChildren = vnodeComponentOptions.children;
opts._componentTag = vnodeComponentOptions.tag;
// 如果传入的 option 中如果有 render,把render相关的也挂载到 $options 上
if (options.render) {
opts.render = options.render;
opts.staticRenderFns = options.staticRenderFns;
}
}
// 返回类的构造函数上最新的options值
// 参数是实例的构造函数 vm.constructor
export function resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor: typeof Component) {
let options = Ctor.options;
// 根实例没有 super,extend 生成的子组件是有
// 如果有 super
if (Ctor.super) {
// 寻找父类的 options
// 通过递归,把上一级父类上最新的 options 更新到变量 superOptions 中。
const superOptions = resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor.super);
// 把 extend 时父类的 options,即 Ctor.superOptions 赋值给 cachedSuperOptions 变量。
const cachedSuperOptions = Ctor.superOptions;
// 如果父类的 options 发生了改变
// 可能是被全局 mixins 混入了其他内容
if (superOptions !== cachedSuperOptions) {
// 更新 options
Ctor.superOptions = superOptions;
// 判断现有子类 option 和在 extend 中挂载到子类 option 中的 sealedOptions是否一样
const modifiedOptions = resolveModifiedOptions(Ctor);
// 更新 extendOptions
if (modifiedOptions) {
extend(Ctor.extendOptions, modifiedOptions);
}
// 然后获取最新的 options
options = Ctor.options = mergeOptions(superOptions, Ctor.extendOptions);
if (options.name) {
options.components[options.name] = Ctor;
}
}
}
// 返回 global-api 里设置的 vue.options
return options;
}
// 判断子类的 options 和从 extend 中挂载的 sealedOptions 是否一致
function resolveModifiedOptions(Ctor: typeof Component): Record<string, any> | null {
let modified;
const latest = Ctor.options;
const sealed = Ctor.sealedOptions;
for (const key in latest) {
if (latest[key] !== sealed[key]) {
if (!modified) modified = {};
modified[key] = latest[key];
}
}
return modified;
}
在 initMixin 函数中,就给 Vue 类的原型上绑定_init 方法。
// 合并 options
// 有子组件时,_isComponent 为true
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// 优化内部组件实例化,因为动态选项合并非常慢,而且没有任何内部组件选项需要特殊处理。
initInternalComponent(vm, options as any)
} else {
// Vue 实例不是组件时
// 就会给$options 属性赋值一个 合并的options
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
// 解析constructor上的options属性的
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor as any),
options || {}, // 传入的 options
vm // 该实例 this
)
}
...
把用户传递的 options 选项与当前构造函数的 options 属性及其父级构造函数的 options 属性进行合并,得到一个新的 options 选项赋值给$options 属性,并将$options 属性挂载到 Vue 实例上
// 给 _renderProxy 属性赋值,不同环境赋值的结果不同
if (__DEV__) {
initProxy(vm);
} else {
// 属性指向 vue 实例本身
vm._renderProxy = vm;
}
我们看了一下 initProxy,其实也是在给 _renderProxy 赋值。全局搜了一下:
// src\core\instance\render.ts
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement);
_renderProxy 是渲染函数 render 的执行上下文,在生产环境下,执行上下文就是实例本身,而在开发环境下,执行上下文则使用 initProxy 进行了处理,这个我们后面再看。
// expose real self
vm._self = vm;
initLifecycle(vm); // 初始化生命周期相关字段
initEvents(vm); // 初始化事件列表
// 处理插槽和作用于插槽,提供_c和$createElement函数用于创建VNode,
// 接收父组件传递$attrs和$listeners作为响应式数据
initRender(vm);
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate', undefined, false /* setContext */); //执行 beforeCreate生命周期钩子
initInjections(vm); // 在 data/props 之前初始化 inject
initState(vm); // // 初始化 data,props,methods computed,watch
initProvide(vm); // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created'); // 执行 created 生命周期钩子
下面的代码,则是调用一些初始化函数来为 Vue 实例初始化一些属性,事件,响应式数据,并且调用了beforeCreate 和 created 的钩子函数
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el);
}
初始化完成以后,会根据是否传入了 el 选项,如果传入了则调用$mount函数进入模板编译与挂载阶段,如果没有传入el选项,则不进入下一个生命周期阶段,需要用户手动执行vm.$mount方法才进入下一个生命周期阶段。
综上 Vue 初始化主要是合并配置,初始化生命周期,初始化事件,初始化渲染,初始化数据等。